Today, companies want to release software faster and with better quality. This is where DevOps helps. DevOps connects development and operations teams so they can work together smoothly.
A key part of DevOps is continuous testing. It makes sure testing happens at every step, not just at the end.
What Is Continuous Testing?
Continuous testing means testing your software again and again at every stage of development.
It gives you quick feedback, so you can fix bugs early before they become big problems.
It combines:
✔ Automation testing
✔ CI/CD pipelines
✔ Quick feedback
✔ Shift-left (testing early)
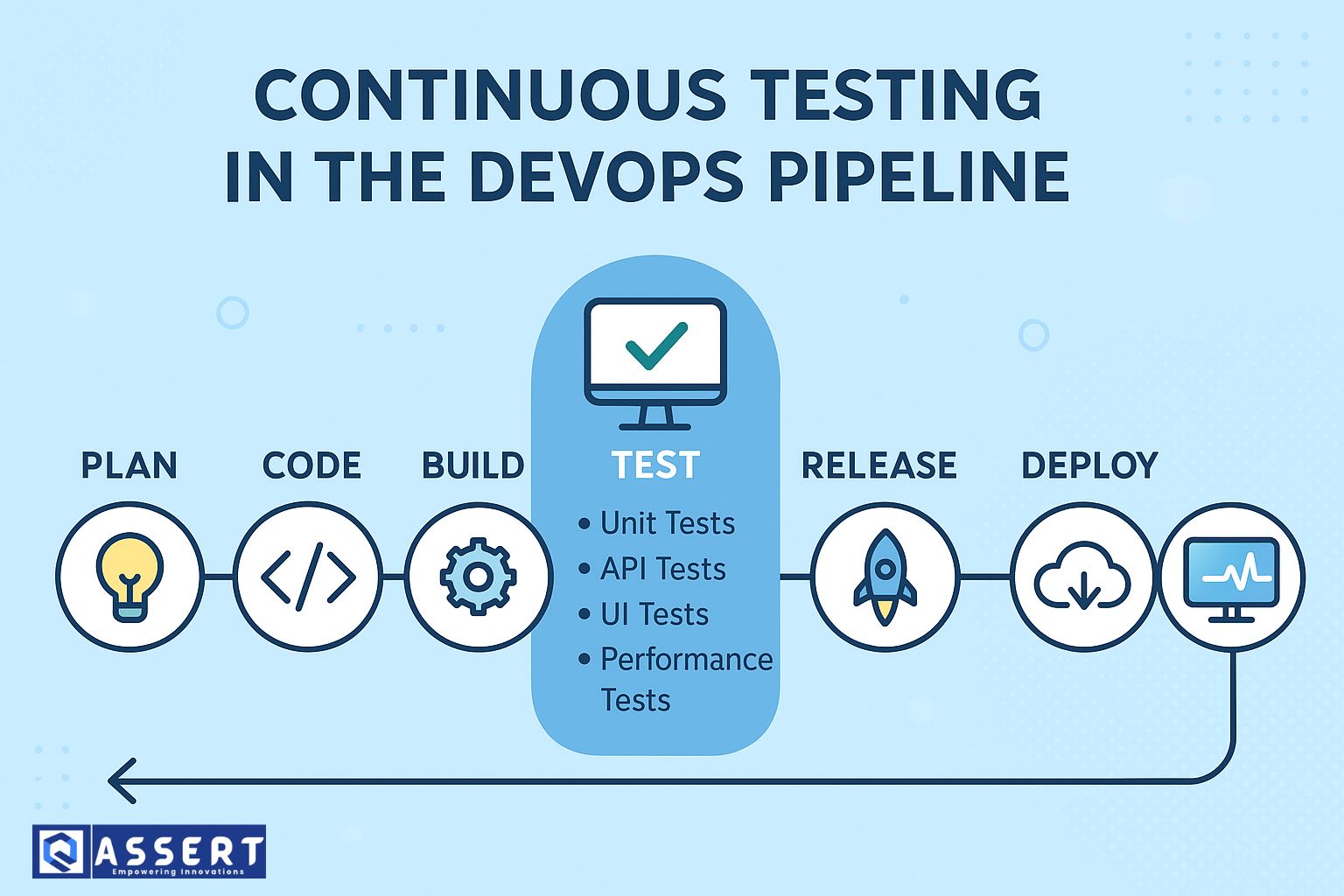
Where Continuous Testing Fits in the DevOps Pipeline
The DevOps pipeline usually has these stages:
-
Plan
-
Code
-
Build
-
Test
-
Release
-
Deploy
-
Monitor
Continuous testing fits into almost all these stages.
1. Planning Stage
Before writing code, teams plan what to build. Testers help by defining:
-
Acceptance criteria
-
Test strategy
-
Risks
-
User expectations
This ensures everyone understands quality from the beginning.
2. Coding Stage
Developers write code and also write small tests called:
-
Unit tests
-
Component tests
These tests run automatically in CI/CD.
When a developer saves code or creates a pull request → tests run immediately.
3. Build Stage
CI tools like:
-
Jenkins → https://www.jenkins.io/
-
GitHub Actions → https://github.com/features/actions
-
GitLab CI → https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/
automatically build the project.
During this build:
✔ Unit tests
✔ API tests
✔ Lint checks
run automatically.
If any test fails → the build stops.
This prevents bad code from moving forward.
4. Testing Stage
This is where most automated tests run:
-
UI tests
-
API tests
-
Functional tests
-
Performance tests
-
Security tests
-
Mobile tests
These tests run on every update to ensure the app works correctly.
5. Release & Deploy Stage
Before deployment, continuous testing checks:
-
Environment configuration
-
API endpoints
-
Smoke tests
-
Database migrations
-
Cloud setup
After deployment, post-deployment tests verify if the app works in real production.
6. Monitoring Stage
After the app is live, monitoring tools check:
-
Errors
-
Crashes
-
Performance
-
User issues
Examples:
-
New Relic → https://newrelic.com/
-
Datadog → https://www.datadoghq.com/
Testers and DevOps team use this data to improve tests and catch hidden issues.
Benefits of Continuous Testing in DevOps
✔ 1. Faster Software Delivery
Tests run automatically, so teams move faster.
✔ 2. Better Quality
Bugs are found early, reducing production issues.
✔ 3. Less Manual Work
Automation reduces repetitive tasks.
✔ 4. Quick Feedback
Teams know instantly if something breaks.
✔ 5. Lower Cost
Fixing bugs early is cheaper than fixing them later.
Best Practices for Continuous Testing
-
Automate as many tests as possible
-
Use CI/CD tools
-
Shift-left testing approach
-
Use parallel test execution
-
Test on real devices and browsers
-
Include performance and security tests
-
Monitor test flakiness
Conclusion
Continuous testing is a key part of the DevOps pipeline. It ensures quality at every step, speeds up releases, and reduces risk. With the help of automation and CI/CD tools, teams can deliver reliable software much faster.