Testing microservices is a critical part of modern software development. As systems become more distributed and services are independently deployed, ensuring that everything works together reliably becomes more complex. This blog covers the key concepts, tools, and strategies to succeed with microservices testing.
Why Testing Microservices Is Different
In a microservices architecture, applications are broken down into smaller services that communicate over APIs. Each service may have its own database, tech stack, and deployment lifecycle.
This independence improves scalability but introduces new challenges for service validation, test environment setup, and system-wide integration.
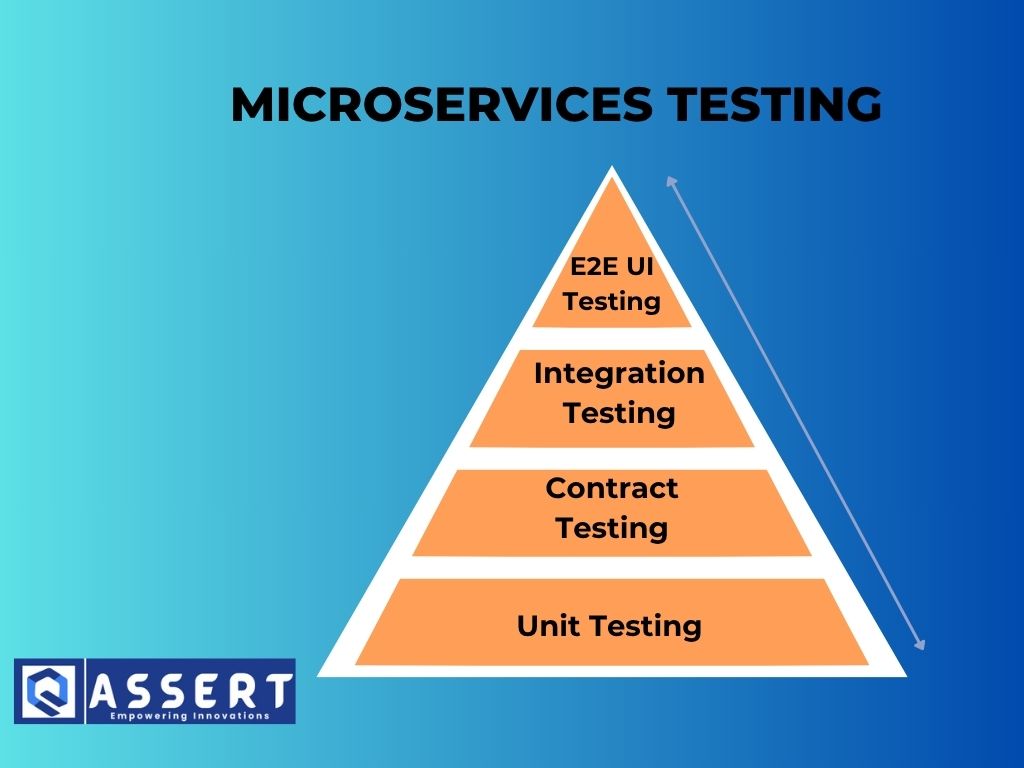
Key Strategies for Testing Microservices
Here are the most effective approaches to cover various test levels in distributed systems:
Unit and Component Testing
These focus on the internal logic of individual services. Use frameworks like JUnit, Mocha, or PyTest for fast, isolated testing.
Contract Testing Between Services
This ensures that API consumers and providers remain compatible over time.
Tool Example:
Pact allows teams to implement consumer-driven contract testing, helping avoid integration failures.
Integration Testing in a Distributed Setup
Integration testing validates how services interact with each other or shared resources like databases or message queues.
Use Docker + Testcontainers to create temporary environments for real-world testing.
End-to-End Testing for Service Chains
End-to-end testing verifies complete business workflows across multiple services and UIs.
Tools: Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress support service-to-UI testing flows.
Tools for Microservices Testing
Here’s a curated list of tools to support your microservices QA process:
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Postman | Manual and automated API tests |
| Rest Assured | Java-based REST API testing |
| WireMock | Mocking and simulating services |
| Pact | Contract testing |
| TestContainers | Real dependencies in Docker |
| k6 | Performance and load testing |
Common Challenges in Microservices Testing
Even with the right strategy, you’ll face these frequent issues:
-
Unstable test environments
-
Data inconsistency across services
-
Slow feedback from end-to-end tests
-
Duplicated test coverage across teams
Practical Tips to Improve Microservices Testing
To make your testing smoother and more reliable:
-
Isolate dependencies with mocks or stubs
-
Automate contract tests and run them in your CI pipeline
-
Monitor services using tools like Prometheus and Jaeger
-
Clean test data after each run using database reset scripts
-
Containerize tests for consistent test environments across dev and CI
Final Thoughts on Testing Microservices
A strong microservices testing strategy involves more than just test cases. It requires architectural awareness, automation discipline, and the right tools. By adopting contract tests, containerized environments, and layered validations, teams can ensure each service—and the system as a whole—works as expected.